Xpansiv Data SDK and API Usage Guide
Overview
This guide demonstrates how to use the Xpansiv Data API to authenticate, download data, and generate insights through visualization. The workflow combines curl commands for API interactions with Python scripting for data analysis and visualization.
1. Obtaining Tokens
Before accessing the Xpansiv Data API, you need to authenticate and obtain access tokens.
Authentication Request:
curl -u 'username:Password' https://api.data.xpansiv.com/auth/loginResponse:
The command will return two tokens:
- Bearer Token - Used for API authorization in subsequent requests
- Refresh Token - Used to obtain new bearer tokens when they expire
Best Practice: Store the bearer token in an environment variable for secure and easy access throughout your session.
export NG_TOKEN="your_bearer_token_here"2. Downloading Data
Once authenticated, you can query the data lake to identify and download files to your local machine.
Searching for Files
The following example searches for files in the placeholder group name "Example Contracts_RECs" and retrieves up to 100 results:
curl \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $NG_TOKEN" \
'https://api.data.xpansiv.com/file/search?size=100&query=groupName%Example%20Contracts_RECs' \
| jq -r '.items[] | "\(.fid),\(.fileName)"' \
| while IFS=',' read -r file_id file_name; do
# Creates a unique file name using the file ID to prevent overwriting
local_file_name="${file_name%.csv}_${file_id}.csv"
echo "Downloading $file_name (ID: $file_id) to $local_file_name..."
curl \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $NG_TOKEN" \
"https://api.data.xpansiv.com/file/$file_id/download" \
> "$local_file_name"
doneWhat This Does:
- Queries the API - Searches for files in the specified group
-
Parses Results
- Uses
jqto extract file IDs and names from the JSON response - Downloads Files - Iterates through each file and downloads it with a unique name based on the file ID
- Prevents Overwriting - Appends the file ID to each filename to ensure uniqueness
Environment Variable: The $NG_TOKEN variable contains your bearer token for authorization.
3. Confirming Files Are Ready
After downloading, verify that the data has been successfully imported to your local machine.
ls -lh *_*.csv
head -n 5 your_downloaded_file.csvTake a quick glance at the files to ensure they were imported properly and aren't corrupted.
4. Drawing Value From Data
Data Filtering
Use Python scripting to filter and prepare your data for analysis. The following example filters based on specific columns:
# Filter data based on PeriodRel and Symbol columns
fdf = df[(df['PeriodRel'].isin(sel_per)) & (df['Symbol'].isin(sel_cont))].copy()Key Columns:
-
PeriodRel- Period relationship/term for the contract -
Symbol- Identifier for the specific asset or contract
You can filter on these columns or others based on your analytical needs. For more information on column terminology specific to Xpansiv Data workflows, please refer to the Data Dictionary section.
Plotting Price With Dates
A significant benefit of the Xpansiv Data system is the ease of accessing and storing data in time series formats. This makes downstream applications like plotting prices against time much simpler.
# Plot data for each contract symbol
for cont in sel_cont:
group = fdf[fdf['Symbol'] == cont]
# Add trace using group['Date'] and group['Mid'] or group['Mid_MA']
# ... plotting code hereWhat This Does:
- Iterates through selected contract symbols
- Filters data for each contract
-
Plots price data (such as
Midprices or moving averagesMid_MA) against dates
Data Points:
-
Mid- Mid-price reflecting the average price for assets -
Mid_MA- Moving average of mid-prices -
Date- Timestamp for each data point
5. Example: Market Insight Visualization
Let's visualize price trends for a specific product and term range.
Scenario: Filter on the product "New Jersey Class 1 REC" for terms 2026 to 2030, then plot contract prices over time.
import streamlit as st
import pandas as pd
import plotly.express as px
# Load downloaded data
df = pd.read_csv('your_downloaded_file.csv')
# Filter for specific product and terms
sel_per = [2026, 2027, 2028, 2029, 2030]
sel_cont = ['NJ_Class1_REC']
fdf = df[(df['PeriodRel'].isin(sel_per)) & (df['Symbol'].isin(sel_cont))].copy()
# Create visualization
fig = px.line(fdf, x='Date', y='Mid', color='Symbol', title='Contract Prices Over Time')
st.plotly_chart(fig)Visualization Tools:
This example uses Streamlit, but you can achieve similar results with:
- Seaborn - Statistical data visualization
- Plotly - Interactive plotting library
- Matplotlib - Basic plotting capabilities
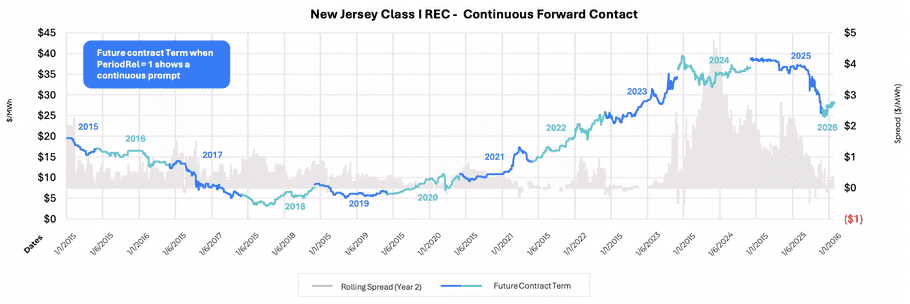
Visualizing price of assets over time using API
Key Benefits
Speed and Scalability: A combination of basic curl commands and simple scripting provides:
- Fast access to market insights
- Scalability to accommodate future data inputs
- Reproducible workflows for ongoing analysis
Time Series Advantages:
- Native time series format simplifies temporal analysis
- Easy plotting of prices against time
- Support for trend analysis and forecasting
API Reference Summary
Authentication Endpoint
POST https://api.data.xpansiv.com/auth/loginFile Search Endpoint
GET https://api.data.xpansiv.com/file/search?size=<size>&query=<query>File Download Endpoint
GET https://api.data.xpansiv.com/file/<file_id>/downloadBest Practices
- Token Security - Always store bearer tokens in environment variables
- File Naming - Use unique identifiers (like file IDs) to prevent overwriting
- Data Validation - Verify downloaded files before processing
- Error Handling - Implement proper error handling in production scripts
- Documentation - Refer to the Data Dictionary for column definitions and terminology
Next Steps
- Explore additional filtering options based on your data columns
- Implement automated data refresh workflows
- Build dashboards for real-time market monitoring
- Integrate with other data sources for comprehensive analysis